Access to Justice
AJS is a system of justice that is compatible with the everyday existence of the people



One of the core principles in the Constitution to guide administration of justice and the exercise of judicial authority is the requirement to embrace alternative forms of dispute resolution, including traditional dispute resolution mechanisms.[1] Article 48 of the Kenyan Constitution guarantees access to justice to all persons in Kenya and if any fee is applicable, then it should be reasonable and not impede access justice. Article 6 of the Constitution provides for Devolution and Access to services for the Kenyans through a devolved government structure making justice a shared responsibility for both the National and County Governments through mutual relations
[1] Robins, Simon (2009). “Restorative Approaches to criminal justice in Africa. Institute for Security Studies.” The theory and practice of criminal justice in Africa. African Human Security Initiative Monograph 161.
79% of the people who have disputes prefer to solve it using non judicial methods.


AJS is a system of justice that is compatible with the everyday existence of the people


Only 21% went to Court to resolve the dispute in 2018


Article 159(2)(c) as the selfexecuting En- forcement of the Right to Culture (Arts. 11 and 44)

Trust is higher in non-public justice institutions than in public justice institutions


Trust is higher in non-public justice institutions than in public justice institutions


Nostrud fact aliquip exrcation nisiut temp sed dui auty.


The Traditional as rational and judicial authority is derived from the people
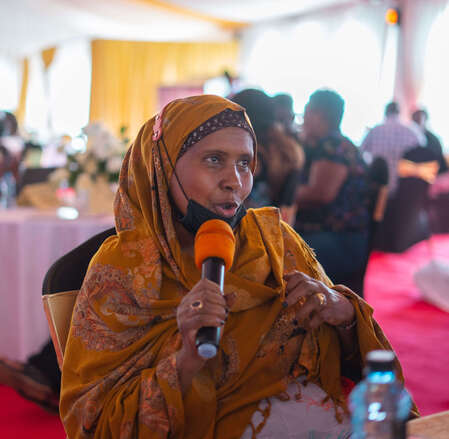

The naming of Alternative Justice Systems was a reconfiguration of miniature judicial character of Alternative Dispute Resolution in Kenya. Most important however, this naming was an apperception of the depth of jurisprudence practiced in most African societies which deals with something beyond mere disputation relationships; It should be known, that this debate of naming is ongoing; Indeed, the author has fronted for the use of the term Multiple Justice Systems The retention of the naming AJS is because justice is understood from the standpoint of the Judiciary as the ultimate guarantor of justice.
AJS are the comprehensive organic, non-state systems of laws, norms, customs, social and legal systems which govern and regulate the entire spectrum of activities and lives of individuals from birth to death. They are constituted, applied and enforced by the people themselves in their own communities. They include dispute resolution mechanisms which we call AJS Mechanisms which does not usually involve using state courts.
Justice (Prof) Joel Ngugi
The National Steering Committee on Implementation of the Alternative Justice Policy (NaSCI-AJS) was gazzetted by the Hon. Chief Justice David Maraga as a multi- stakeholder Committee to spearhead the implementation of the AJS Policy.
Be the first one to receive latest updates.

Leave a Comment